Let’s face it: what you eat before and after a workout can make or break your results. Whether you’re aiming for muscle gain, fat loss, or both, nailing your nutrition is just as important as lifting weights or hitting the treadmill. But with so much conflicting advice out there, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed.
Don’t worry—I’ve got you covered. In this post, we’ll break down the science-backed strategies for fueling your body before and after exercise. By the end, you’ll know exactly what to eat to maximize your results. Let’s dive in!
Why Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition Matters
Your body is like a high-performance car. You wouldn’t expect it to run smoothly without the right fuel, right? The same goes for your workouts.
- Pre-Workout Nutrition: Fuels your performance, boosts energy, and prevents muscle breakdown.
- Post-Workout Nutrition: Repairs muscle tissue, replenishes energy stores, and kickstarts recovery.
The key is tailoring your meals to your goals—whether that’s building muscle, burning fat, or both. Let’s explore how to do that.
Pre-Workout Nutrition: Fueling Your Performance
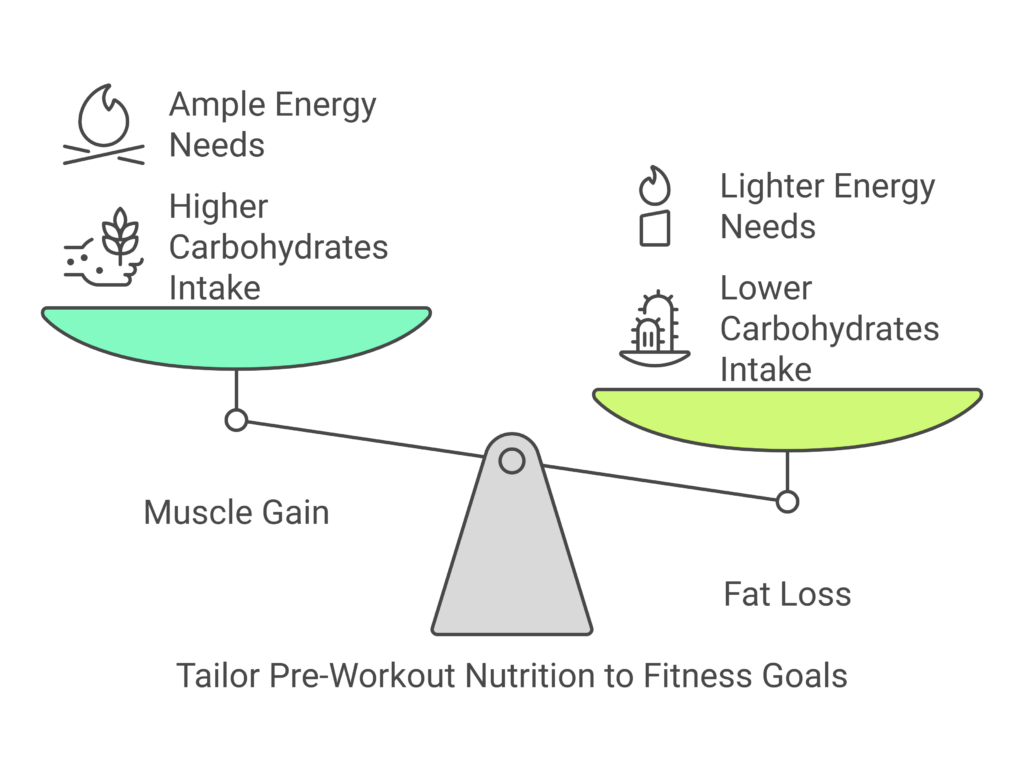
For Muscle Gain
If your goal is to pack on muscle, your pre-workout meal should focus on providing sustained energy and ample protein to support muscle protein synthesis.
Timing: 30-60 minutes before training
Macronutrient Targets:
- Carbohydrates: 0.5g/kg body weight (about 34g for a 150lb person)
- Protein: 20-30g
Best Food Combinations:
| Food Category | Examples | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Complex Carbs | Oats, sweet potatoes, quinoa | Sustained energy release |
| Fast-Digesting Protein | Whey isolate, egg whites | Rapid amino acid availability |
| Performance Enhancers | Bananas, beetroot juice | Nitric oxide boost + quick carbs |
Sample Meals:
- Oatmeal with whey protein and blueberries
- Chicken breast with white rice and steamed veggies
- Greek yogurt with honey and almonds
For Fat Loss
If fat loss is your goal, your pre-workout meal should be lighter but still provide enough energy to power through your session.
Timing: 30-60 minutes before training (or fasted)
Macronutrient Targets:
- Carbs: ≤0.25g/kg body weight
- Protein: 20-30g
Optimal Choices:
| Food Type | Examples | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Carb Proteins | Eggs, cottage cheese, turkey | Maintains muscle while cutting |
| Fibrous Veggies | Spinach, broccoli, zucchini | Volume eating without excess calories |
| Strategic Fats | Almond butter, avocado | Controlled energy release |
Sample Meals:
- Scrambled eggs with spinach
- Protein shake with almond milk
- Apple slices with peanut butter (≤1 tbsp)
Post-Workout Nutrition: Recovery and Growth
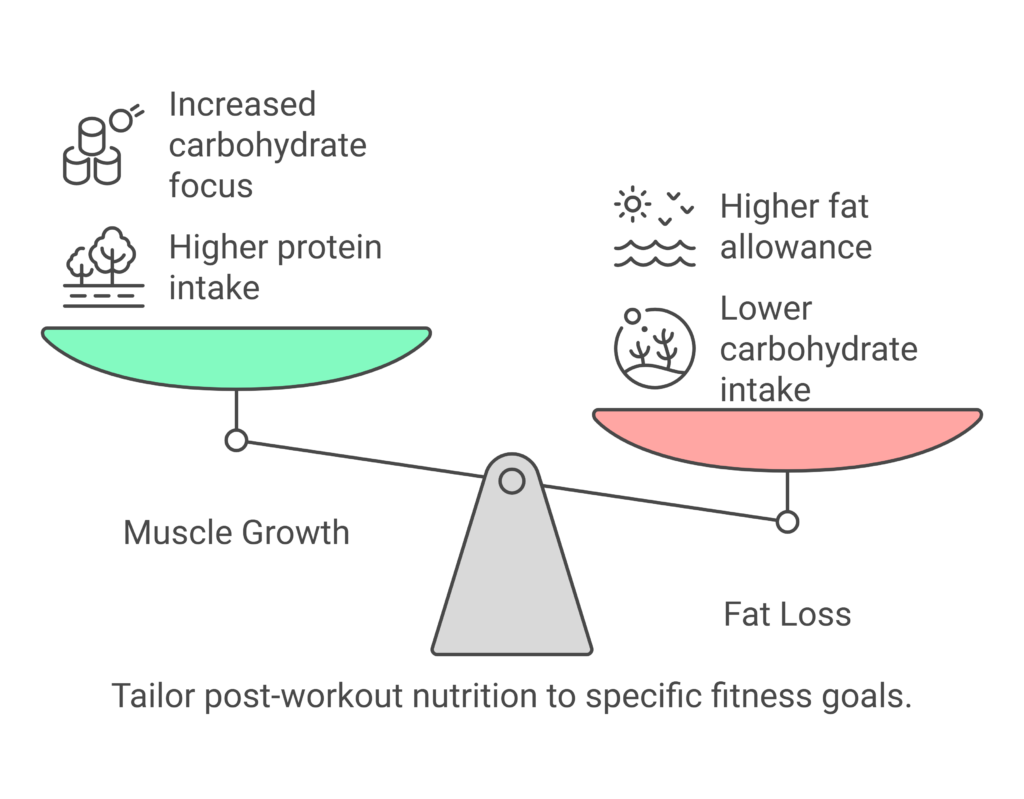
For Muscle Growth
After a workout, your muscles are primed for repair and growth. Your post-workout meal should focus on replenishing glycogen stores and providing high-quality protein.
Anabolic Window: 0-2 hours post-training
Macronutrient Targets:
- Protein: 30-40g (0.4-0.5g/kg)
- Carbs: 0.5-0.7g/kg
- Fats: ≤10g
Optimal Foods:
| Category | Examples | Muscle-Building Mechanism |
|---|---|---|
| Complete Proteins | Chicken, salmon, whey | Maximizes MPS (muscle protein synthesis) |
| High-GI Carbs | White rice, potatoes | Rapid glycogen replenishment |
| Recovery Additives | Tart cherry juice, turmeric | Reduces inflammation |
Sample Meals:
- Grilled salmon with jasmine rice and asparagus
- Protein pancakes with maple syrup
- Muscle Mac macaroni with lean ground turkey
For Fat Loss
If you’re cutting calories, your post-workout meal should still prioritize protein to preserve muscle mass while keeping carbs and fats in check.
Metabolic Window: 0-45 minutes post-training
Macronutrient Targets:
- Protein: 20-30g
- Carbs: 0.25g/kg
- Fats: 10-15g
Strategic Choices:
| Food Type | Examples | Metabolic Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Lean Proteins | White fish, shrimp, tofu | High thermic effect |
| Low-GI Carbs | Quinoa, berries, lentils | Sustained energy without spikes |
| Healthy Fats | Chia seeds, olive oil | Supports hormone balance |
Sample Meals:
- Grilled chicken salad with quinoa and olive oil
- Protein smoothie with spinach and almond butter
- Tuna lettuce wraps with sweet potato wedges
Science-Backed Nutrition Timing
To make things even clearer, here’s a timeline for optimizing your pre- and post-workout nutrition:
| Time Frame | Muscle Gain Protocol | Fat Loss Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| 2-3 Hours Pre | 400-600 kcal meal | 200-300 kcal snack |
| 30-60 Min Pre | Carb+protein shake | BCAA + caffeine |
| Immediately Post | 1:2 protein:carb ratio | 2:1 protein:carb ratio |
| 2 Hours Post | Whole food recovery meal | Balanced low-cal meal |
Key Research Findings
- Pre-workout carbs improve training volume by 18-22% compared to fasted workouts.
- Post-workout protein timing increases muscle growth by 26%.
- Strategic carb cycling maintains metabolic rate during calorie deficits.
- Combining multiple protein sources boosts amino acid availability by 40%.
The Role of Hydration in Workout Performance
Hydration is often overlooked but plays a critical role in both performance and recovery.
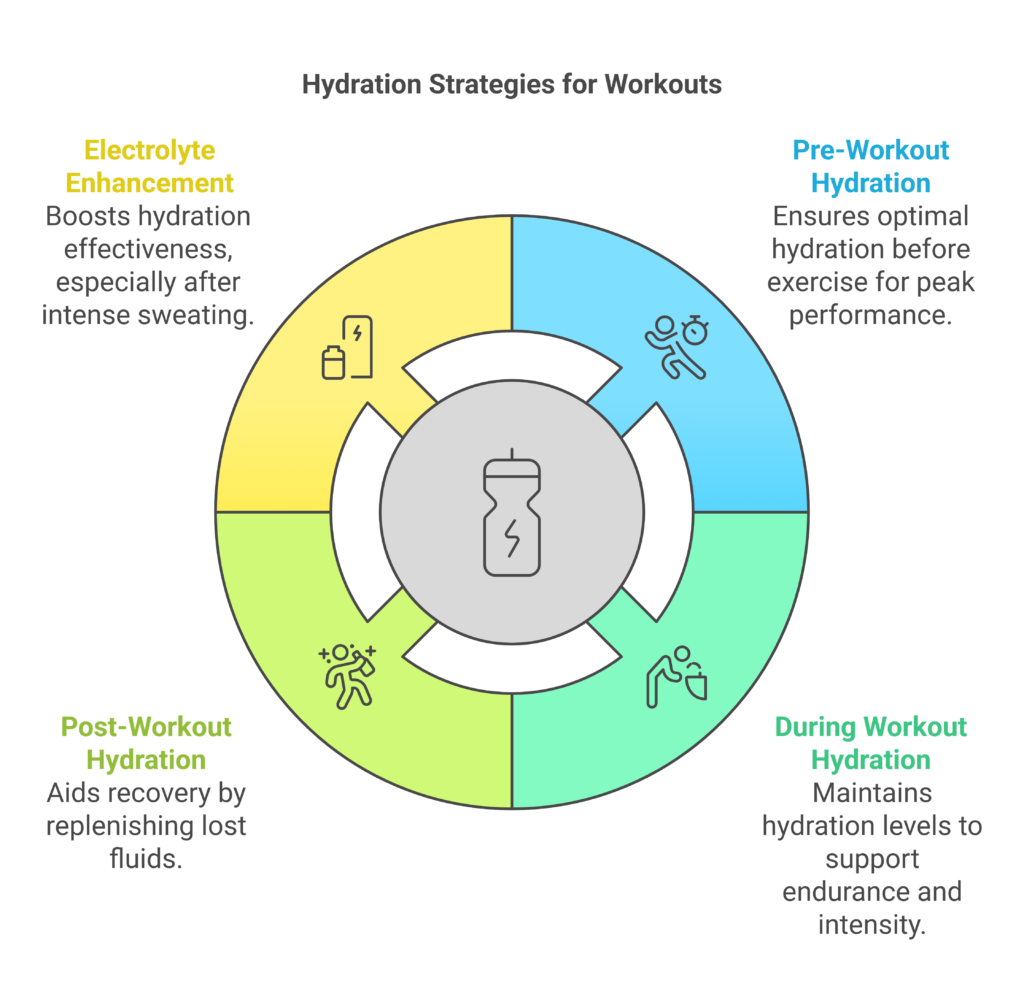
- Pre-Workout: Drink 16-20 ounces of water 2-3 hours before exercise and another 8-10 ounces 20-30 minutes before.
- During Workout: Sip 7-10 ounces every 10-20 minutes, especially during intense or long sessions.
- Post-Workout: Replenish fluids by drinking 16-24 ounces for every pound lost during exercise.
Adding electrolytes (like sodium and potassium) can further enhance hydration, especially if you’re sweating heavily.
Supplements to Consider
While whole foods should always be your foundation, certain supplements can enhance your results:
- Protein Powder: Convenient way to hit your protein targets, especially post-workout.
- Creatine: Supports strength and muscle growth, particularly for high-intensity training.
- Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs): Helps reduce muscle soreness and preserve muscle mass during calorie deficits.
- Caffeine: Boosts energy and focus for your workouts.
Remember, supplements are just that—supplements. They should complement, not replace, a balanced diet.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Skipping Pre-Workout Nutrition
Exercising on an empty stomach can lead to fatigue, poor performance, and muscle breakdown. Even a small snack can make a big difference.
2. Overloading on Protein
While protein is essential, consuming excessive amounts won’t speed up muscle growth. Stick to the recommended 20-40g per meal.
3. Ignoring Carbs Post-Workout
Carbs are crucial for replenishing glycogen stores. Don’t fear them—even if you’re aiming for fat loss.
4. Neglecting Recovery
Your body needs time to repair and grow. Prioritize sleep, hydration, and stress management alongside your nutrition.
Tailoring Nutrition to Your Workout Type
Different workouts require different fueling strategies:
- Strength Training: Prioritize protein and carbs to support muscle repair and growth.
- Cardio: Focus on easily digestible carbs for quick energy and moderate protein for recovery.
- HIIT: Balance carbs and protein to fuel intense bursts of effort and aid recovery.
Whether you’re chasing muscle gain, fat loss, or both, your nutrition strategy should align with your goals. Remember:
- Pre-workout meals fuel your performance.
- Post-workout meals repair and rebuild.
- Timing and macronutrient balance are key to maximizing results.
So, the next time you hit the gym, make sure you’re armed with the right fuel. Your body (and your progress) will thank you!
Let’s crush those goals—one meal at a time!
References:
- Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition for Muscle Gain and Fat Loss
- Best Pre-Workout Meals for Muscle Gain
- Post-Workout Nutrition Tips
- What to Eat Before a Workout for Fat Loss


